 On Page SEO Step by Step – Learn the fundamentals of optimization your webpages for search engines with our comprehensive guide. From keyword research to content optimization and technical tweaks, discover the essential steps to improve your website’s visibility and rankings.
On Page SEO Step by Step – Learn the fundamentals of optimization your webpages for search engines with our comprehensive guide. From keyword research to content optimization and technical tweaks, discover the essential steps to improve your website’s visibility and rankings.
Keyword Research:
Keyword research is the foundation of any successful SEO strategy. Here’s how you can conduct keyword research effectively:

- Understand Your Niche and Audience:
- Start by understanding your target audience and the topics relevant to your niche. Consider what questions they might have or what terms they would use to search for information related to your business or website.
- Brainstorm Seed Keywords:
- Begin with a few seed keywords that are directly related to your business, products, or services. These are broad terms that represent the core topics of your website.
- Use Keyword Research Tools:
- Utilize keyword research tools such as Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Ahrefs, Ubersuggest, or Moz Keyword Explorer. These tools provide data on search volume, keyword difficulty, and related keywords.
- Generate Keyword Ideas:
- Enter your seed keywords into the keyword research tool to generate a list of related keywords and phrases. Look for terms with a balance of search volume (how many people are searching for them) and competition.
- Analyze Keyword Metrics:
- Evaluate each keyword based on metrics like search volume, keyword difficulty, and relevance to your content. Aim for keywords with sufficient search volume and lower competition.
- Consider Long-Tail Keywords:
- Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that often have lower search volume but higher conversion rates. Incorporate a mix of long-tail keywords and broader terms into your content strategy.
- Assess Keyword Intent:
- Consider the intent behind each keyword. Are users looking for information, products, services, or solutions? Tailor your content to match the searcher’s intent for better engagement and conversion.
- Competitor Analysis:
- Analyze the keywords that your competitors are ranking for. Identify opportunities where you can compete or areas where you can differentiate your content.
- Refine and Prioritize Keywords:
- Refine your list of keywords based on relevance, search volume, competition, and user intent. Prioritize keywords that align closely with your business goals and have the potential to drive meaningful traffic.
- Create Keyword Mapping:
- Organize your keywords into groups or themes and map them to specific pages or topics on your website. This helps ensure that each page targets a unique set of keywords and topics.
Title Tag Optimization On Page SEO:
Title tag optimization is crucial for on-page SEO because it directly impacts your search engine visibility and click-through rates. Here’s how to optimize your title tags effectively:

- Include Target Keyword:
- Incorporate your primary target keyword naturally into the title tag. This helps search engines understand the topic of your page and improves its relevance for related searches.
- Craft Compelling Titles:
- Create titles that are descriptive, compelling, and relevant to the content of your page. Aim to capture the user’s attention and entice them to click on your link in search results.
- Keep it Concise:
- Limit your title tag to around 50-60 characters to ensure it displays fully in search engine results pages (SERPs). This prevents truncation and ensures that your title is easily readable.
- Front-load Keywords:
- Place your target keyword near the beginning of the title tag whenever possible. This gives it more prominence and relevance to search engines and users.
- Brand Name:
- Include your brand name at the end of the title tag, especially if your brand is well-known or relevant to the content. This helps reinforce your brand identity and can improve click-through rates for branded searches.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing:
- While it’s important to include your target keyword, avoid keyword stuffing or cramming multiple keywords into the title tag unnaturally. This can have a negative impact on both user experience and SEO.
- Unique Titles for Each Page:
- Ensure that each page on your website has a unique title tag that accurately reflects its content. This helps prevent confusion for users and allows search engines to differentiate between pages.
- Match Title with Content:
- Make sure that the title tag accurately represents the content of the page. Misleading or clickbait titles can lead to high bounce rates and a negative impact on your site’s credibility.
- Use Title Tag Formulas:
- Experiment with proven title tag formulas, such as including numbers, power words, or emotional triggers, to increase engagement and click-through rates. However, always prioritize relevance and clarity over gimmicks.
- Test and Iterate:
- Continuously monitor the performance of your title tags using analytics tools. Test different variations and iterations to see which titles resonate best with your audience and drive the highest click-through rates.
Meta Description Optimization On Page SEO:
Meta description optimization is essential for improving click-through rates and providing users with a preview of your page’s content in search engine results. Here’s how to optimize your meta descriptions effectively:

- Write Compelling Descriptions:
- Craft concise and engaging meta descriptions that accurately summarize the content of your page. Aim to capture the user’s attention and entice them to click on your link.
- Include Target Keywords:
- Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into the meta description. While meta descriptions don’t directly impact search rankings, including keywords can help reinforce the relevance of your page to search queries.
- Keep it Within Character Limit:
- Limit your meta description to around 150-160 characters to ensure it displays fully in search engine results pages (SERPs). This prevents truncation and ensures that your description is easily readable.
- Highlight Unique Selling Points:
- Highlight the unique value proposition or key benefits of your page to encourage clicks. Clearly communicate what sets your content apart from others and why users should choose to visit your page.
- Match Content and User Intent:
- Ensure that your meta description accurately reflects the content of your page and aligns with the user’s search intent. Misleading or irrelevant descriptions can lead to high bounce rates and a negative user experience.
- Use Actionable Language:
- Use action-oriented language and calls-to-action (CTAs) to prompt users to take the desired action, such as “Learn More,” “Get Started,” or “Download Now.” This can help increase engagement and click-through rates.
- Avoid Duplicate Descriptions:
- Ensure that each page on your website has a unique meta description that corresponds to its specific content. Avoid using duplicate or boilerplate descriptions, as this can lead to confusion for users and search engines.
- Optimize for Rich Snippets:
- If applicable, optimize your meta description to appear as a rich snippet in search results. This may involve including structured data markup or specific formatting to enhance the appearance of your listing.
- Test and Iterate:
- Continuously monitor the performance of your meta descriptions using analytics tools. Test different variations and iterations to see which descriptions resonate best with your audience and drive the highest click-through rates.
- Stay Updated:
- Regularly review and update your meta descriptions to ensure they remain accurate and relevant over time. Changes in search algorithms, user behavior, or your content may necessitate updates to your meta descriptions.
Heading Tags (H1, H2, etc.) On Page SEO:
Heading tags, such as H1, H2, H3, etc., are HTML elements used to structure the content of a web page hierarchically. They play a crucial role in on-page SEO by providing search engines with information about the structure and hierarchy of your content. Here’s how to optimize heading tags effectively:

- Use H1 for Main Title:
- Each web page should have one main H1 heading that represents the primary title or headline of the page. This heading should accurately summarize the main topic or purpose of the page and ideally include your target keyword.
- Organize Content with H2, H3, etc.:
- Use subsequent heading tags (H2, H3, H4, etc.) to organize the content hierarchically into sections and subsections. These headings should logically divide the content and provide a clear outline for readers and search engines.
- Include Keywords Naturally:
- Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into your heading tags where appropriate. However, avoid keyword stuffing and prioritize readability and user experience.
- Maintain Consistency:
- Maintain consistency in your heading hierarchy throughout the page and across your website. Use a logical and structured approach to organizing your content to make it easy for both users and search engines to navigate.
- Optimize for Readability:
- Ensure that your heading tags are easy to read and understand. Use descriptive and concise headings that accurately reflect the content of each section.
- Avoid Skipping Heading Levels:
- Follow a sequential order when using heading tags (e.g., H1 followed by H2, then H3, etc.). Avoid skipping heading levels, as this can create confusion for both users and search engines.
- Use CSS for Styling:
- Use CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) to control the visual appearance of your heading tags, such as font size, color, and style. This allows you to customize the design while maintaining the semantic structure of your content.
- Include Related Keywords:
- While the main focus should be on your primary keyword, consider including related keywords or variations in your heading tags to provide additional context to search engines.
- Optimize for Voice Search:
- With the rise of voice search, consider how users might phrase their queries conversationally. Optimize your heading tags to address common questions or queries that users might voice search for.
- Test and Iterate:
- Monitor the performance of your heading tags using analytics tools. Test different variations and iterations to see which headings resonate best with your audience and contribute to improved search visibility.
Keyword Placement On Page SEO:
- Incorporate your target keywords naturally and seamlessly into your content. Avoid forcing keywords into sentences where they don’t fit or sacrificing readability for the sake of optimization.

-
- Title Tag:
- Include your primary keyword in the title tag of your webpage. This helps search engines understand the topic of your page and improves its relevance for related searches.
- Meta Description:
- While meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, including keywords in the meta description can reinforce the relevance of your page for specific search queries.
- Heading Tags (H1, H2, etc.):
- Use heading tags (H1 for main title, H2, H3, etc. for subheadings) to structure your content logically. Include your target keyword in at least one heading tag to signal its importance to search engines.
- First Paragraph:
- Include your primary keyword in the first paragraph of your content. This establishes relevance early on and provides clarity to both users and search engines about the topic of your page.
- Throughout the Body:
- Sprinkle your target keywords naturally throughout the body of your content. Aim for a balanced distribution and avoid overstuffing keywords, as this can negatively impact readability and user experience.
- Anchor Text:
- When linking internally or externally, use keyword-rich anchor text that accurately describes the linked page’s content. This can help improve the relevance of both the linking page and the linked-to page for specific keywords.
- Image Alt Text:
- Optimize image alt text by including relevant keywords where appropriate. This helps search engines understand the content of your images and can improve your page’s visibility in image search results.
- URL Structure:
- Incorporate keywords into the URL structure of your web pages, if possible. Use descriptive and keyword-rich URLs that clearly indicate the content of the page.
- Meta Keywords (Optional):
- While meta keywords are no longer a significant ranking factor, you can still include them in the meta tags of your webpage. However, focus more on optimizing other on-page elements for keywords.
- User Experience Comes First:
- Prioritize user experience and readability over keyword placement. While keywords are important for SEO, creating valuable, informative, and engaging content should always be your primary goal.
- Monitor and Adjust:
- Regularly monitor your keyword placement and performance using analytics tools. Adjust your strategy as needed based on changes in search trends, user behavior, and search engine algorithms.
- Title Tag:
Quality Content On Page SEO:
Creating high-quality content is essential for successful SEO and overall user satisfaction. Here are some key aspects of producing quality content:

- Relevance:
- Ensure your content is relevant to your target audience and aligned with their interests, needs, and search intent. Conduct thorough research to understand your audience’s preferences and pain points.
- Value:
- Provide valuable and informative content that addresses the questions, concerns, or problems of your audience. Offer unique insights, practical tips, expert advice, or entertaining content that adds genuine value.
- Originality:
- Aim to create original and unique content that stands out from the competition. Avoid duplicating content from other sources or engaging in plagiarism. Offer fresh perspectives, research, or personal experiences to differentiate your content.
- Accuracy:
- Ensure the information presented in your content is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date. Verify facts, cite credible sources, and avoid spreading misinformation or outdated data.
- Clarity and Readability:
- Make your content easy to understand and digest by using clear and concise language. Break up long paragraphs into shorter sentences and use subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists to improve readability.
- Engagement:
- Create content that captivates and engages your audience. Use storytelling, visuals, multimedia elements (such as images, videos, infographics), and interactive features to enhance engagement and keep users on your site longer.
- Authority:
- Establish your expertise and authority in your niche by providing well-researched, authoritative content. Demonstrate your credibility through in-depth analysis, case studies, testimonials, and industry recognition.
- User Experience:
- Prioritize user experience by ensuring your content is easy to access, navigate, and consume across different devices and screen sizes. Optimize loading speed, mobile responsiveness, and site architecture to enhance user satisfaction.
- Call to Action (CTA):
- Include clear and compelling calls to action (CTAs) to prompt users to take the desired action, whether it’s signing up for a newsletter, downloading a resource, making a purchase, or engaging with your content further.
- Feedback and Iteration:
- Solicit feedback from your audience and monitor engagement metrics, such as bounce rate, time on page, and social shares, to gauge the effectiveness of your content. Use this feedback to iterate and improve future content.
- Optimized for Search Engines:
- While creating quality content for users is paramount, ensure it is also optimized for search engines. Incorporate relevant keywords naturally, optimize meta tags, headings, and other on-page elements, and follow SEO best practices to improve visibility in search results.
Image Optimization On Page SEO:
Image optimization is crucial for improving website performance, user experience, and search engine visibility. Here’s how to optimize images effectively:

- Choose the Right Format:
- Select the appropriate image format based on the type of image and its intended use. Use JPEG for photographs and images with many colors, PNG for images with transparency or text, and SVG for simple graphics and logos.
- Compress Images:
- Compress images to reduce file size without significantly compromising quality. Use tools like Adobe Photoshop, TinyPNG, or ImageOptim to compress images before uploading them to your website.
- Resize Images:
- Resize images to the appropriate dimensions for their display on your website. Avoid uploading oversized images and use CSS to resize them dynamically if needed.
- Optimize Alt Text:
- Include descriptive and keyword-rich alt text for each image. Alt text helps visually impaired users understand the content of images and improves accessibility. Additionally, search engines use alt text to understand the context of images for indexing and ranking purposes.
- Use Descriptive Filenames:
- Rename image files with descriptive filenames that include relevant keywords. Avoid generic filenames like “IMG_1234.jpg” and instead use descriptive names that accurately reflect the content of the image.
- Utilize Title Attribute:
- Optionally, use the title attribute to provide additional context or information about an image when users hover over it. While not as crucial for SEO as alt text, the title attribute can improve user experience.
- Implement Lazy Loading:
- Implement lazy loading to defer the loading of offscreen images until they are needed. This can improve page load times and reduce bandwidth usage, especially on pages with many images.
- Enable Image Compression:
- Enable server-side image compression if available, such as Gzip compression or Brotli compression. This further reduces image file sizes and improves website performance.
- Use Responsive Images:
- Implement responsive image techniques to serve appropriately sized images based on the user’s device and screen size. This ensures optimal display quality and performance across different devices.
- Optimize Thumbnails:
- If your website uses thumbnails or preview images, ensure they are optimized for fast loading and provide a clear representation of the full-sized image.
- Monitor Image Performance:
- Regularly monitor the performance of your images using website performance monitoring tools or Google PageSpeed Insights. Identify any large or uncompressed images that may be slowing down your website.
Internal Linking On Page SEO:
Internal linking is a fundamental aspect of on-page SEO and website architecture. It involves linking from one page of your website to another page within the same domain. Here’s how to effectively implement internal linking:
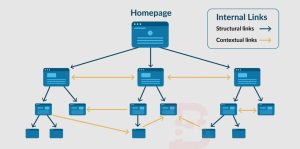
- Understand the Purpose:
- Internal linking serves multiple purposes, including distributing page authority, guiding users to relevant content, and helping search engines discover and understand the structure of your website.
- Create a Hierarchical Structure:
- Organize your website’s content into a hierarchical structure with main categories, subcategories, and individual pages. This helps establish a clear navigation path for users and search engines.
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text:
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text when creating internal links. Anchor text helps both users and search engines understand the context and relevance of the linked page.
- Link to Relevant Pages:
- Link from one page to another page that is contextually relevant and provides additional value to the user. Avoid linking to pages randomly or excessively, as this can dilute the effectiveness of your internal linking strategy.
- Prioritize Important Pages:
- Prioritize internal links to important pages that you want to rank higher in search results or pages that you want to drive more traffic to. These may include cornerstone content, landing pages, or product pages.
- Deep Linking:
- Practice deep linking by linking to specific sections or subsections within a page, rather than just the homepage or main category pages. This helps distribute link equity and provides users with more targeted information.
- Create Content Silos:
- Group related content into thematic clusters or silos and interlink them strategically. This helps establish topical relevance and strengthens the authority of individual pages within the same topic cluster.
- Audit and Update Internal Links:
- Regularly audit your website’s internal links to ensure they are functional, relevant, and up-to-date. Remove or update broken links, and identify opportunities to add new internal links where appropriate.
- Use Navigation Menus and Footer Links:
- Incorporate internal links into your website’s navigation menus and footer links. This provides users with easy access to important pages and improves site usability.
- Link Naturally and Contextually:
- Incorporate internal links naturally within the body of your content where they add value to the user experience. Avoid forcing or over-optimizing internal links, as this can appear spammy to both users and search engines.
- Monitor Performance and Adjust:
- Monitor the performance of your internal links using analytics tools. Track metrics such as click-through rates, time on page, and conversion rates to evaluate the effectiveness of your internal linking strategy. Adjust your strategy based on data and user feedback.
External Linking On Page SEO:
External linking, also known as outbound linking, involves linking from your website to other websites on the internet. Here’s how to effectively implement external linking:
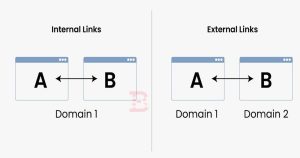
- Link to High-Quality, Relevant Websites:
- Link to authoritative and reputable websites that provide valuable information relevant to your content. Choose websites that enhance the user experience and add credibility to your own content.
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text:
- Use descriptive and meaningful anchor text when linking to external websites. The anchor text should accurately describe the linked page’s content and provide context to users and search engines.
- Avoid Over-Linking:
- Avoid excessive external linking, especially to low-quality or irrelevant websites. Over-linking can dilute the value of your content and may be perceived as spammy by search engines.
- Open Links in New Tab (Optional):
- Consider opening external links in a new tab or window, especially if you don’t want users to navigate away from your website. This allows users to explore external content without leaving your site entirely.
- Check for Broken Links:
- Regularly check for broken or outdated external links on your website. Use tools like Google Search Console or online link checkers to identify and fix broken links to maintain a positive user experience.
- Attribute Nofollow for Untrusted Links:
- Consider adding the rel=”nofollow” attribute to external links that you don’t fully trust or endorse. This tells search engines not to pass PageRank to the linked website, which can help mitigate the risk of associating with spammy or low-quality sites.
- Provide Additional Resources:
- Use external links to provide additional resources, references, or further reading for your audience. This adds value to your content and enhances user engagement.
- Build Relationships with Webmasters:
- Reach out to webmasters of the websites you link to and establish relationships. Building connections with other website owners can lead to opportunities for collaboration, guest blogging, and reciprocal linking.
- Use Citations and Attribution:
- When referencing statistics, research findings, or quotes from external sources, provide proper citations and attribution. This demonstrates transparency and integrity, and it also avoids potential copyright issues.
- Consider User Intent:
- Keep user intent in mind when selecting external links. Choose websites that align with the interests and needs of your audience, and provide them with valuable information or resources that complement your own content.
- Monitor and Update Links:
- Regularly monitor the external links on your website and update them as needed. Ensure that linked websites are still relevant, trustworthy, and provide accurate information.
Mobile-Friendliness On Page SEO:
Design your website with a mobile-first mindset, prioritizing simplicity, clarity, and ease of use for mobile users. Use larger font sizes, clear navigation menus, and touch-friendly buttons and links to improve usability on small screens.

-
- Optimize Loading Speed:
- Optimize your website’s loading speed for mobile devices by minimizing file sizes, leveraging browser caching, and reducing server response times. Faster loading times improve user experience and reduce bounce rates, especially on mobile devices with slower internet connections.
- Optimize Images and Media:
- Compress images and optimize media files to reduce their file sizes without compromising quality. Use formats like WebP for images and lazy loading techniques to prioritize the loading of visible content and defer offscreen images and media until they’re needed.
- Readable Text and Content:
- Ensure that text content is readable without zooming or horizontal scrolling on mobile devices. Use legible font sizes, adequate line spacing, and appropriate contrast between text and background colors. Break up long paragraphs into shorter, digestible chunks to improve readability.
- Optimize Tap Targets:
- Make sure that clickable elements, such as buttons, links, and form fields, are sufficiently large and spaced apart to accommodate touch interactions. Aim for a minimum tap target size of 48×48 CSS pixels to prevent accidental clicks and improve usability.
- Avoid Flash and Pop-ups:
- Avoid using Flash content, pop-ups, or interstitials that are disruptive or incompatible with mobile devices. These elements can hinder navigation, slow down page loading, and create a poor user experience on mobile.
- Test Across Devices:
- Test your website’s mobile-friendliness across a variety of devices, browsers, and operating systems to ensure consistent performance and compatibility. Use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and browser developer tools to identify and fix any issues.
- Utilize Mobile SEO Best Practices:
- Implement mobile SEO best practices, such as optimizing meta tags, ensuring crawlability and indexability, and prioritizing mobile-friendly content formats like AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) for faster loading on mobile devices.
- Monitor Performance and User Behavior:
- Monitor key performance metrics, such as bounce rate, time on page, and conversion rates, for mobile users separately. Use analytics tools to identify areas for improvement and optimize your website’s mobile experience based on user behavior and feedback.
- Optimize Loading Speed:
Page Speed Optimization On Page SEO:
Page speed optimization is crucial for providing a positive user experience, reducing bounce rates, and improving search engine rankings. Here’s how to optimize the speed of your web pages:
- Minimize HTTP Requests:
- Reduce the number of HTTP requests by combining and minifying CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files. Use tools like Minify, UglifyJS, or CSSNano to streamline your code and remove unnecessary characters, whitespace, and comments.
- Optimize Images:
- Compress and optimize images to reduce their file sizes without sacrificing quality. Use tools like Photoshop, TinyPNG, or ImageOptim to compress images before uploading them to your website. Consider using next-generation image formats like WebP for even smaller file sizes.
- Enable Browser Caching:
- Leverage browser caching to store static resources, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files, locally on the user’s device. Set an appropriate expiration period for cacheable resources to reduce the need for repeated downloads and improve page load times for returning visitors.
- Reduce Server Response Time:
- Optimize your server configuration, database queries, and backend code to minimize server response time. Use caching mechanisms, content delivery networks (CDNs), and server-side caching solutions to reduce latency and speed up content delivery.
- Enable Gzip Compression:
- Enable Gzip compression to compress text-based resources, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, before sending them over the network. Gzip compression can significantly reduce file sizes and improve page load times, especially for text-heavy websites.
- Minimize Render-Blocking Resources:
- Identify and prioritize critical rendering paths to minimize the impact of render-blocking resources, such as external CSS and JavaScript files. Load essential CSS inline and defer non-essential scripts to improve initial rendering and page interactivity.
- Optimize Critical Rendering Path:
- Optimize the critical rendering path by prioritizing the loading of above-the-fold content and deferring the loading of non-essential resources. Use techniques like lazy loading, asynchronous loading, and resource hints to improve perceived performance and user engagement.
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
- Utilize content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute static resources across multiple servers and edge locations worldwide. CDNs cache content closer to the user’s location, reducing latency and improving page load times for visitors from different geographic regions.
- Prioritize Above-the-Fold Content:
- Prioritize the loading of above-the-fold content, including text, images, and interactive elements, to improve perceived performance and user engagement. Use asynchronous loading and lazy loading techniques to defer offscreen content until it’s needed.
- Monitor Performance and Optimize Continuously:
- Regularly monitor your website’s performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or WebPageTest. Identify performance bottlenecks and opportunities for optimization, and implement changes to improve page speed and overall user experience.
Schema Markup On Page SEO:
Schema markup, also known as structured data, is a form of code that you can add to your website to help search engines understand the content and context of your pages better. It provides additional information about your content, enabling search engines to display more informative and visually appealing search results. Here’s how to implement schema markup effectively:

- Understand Schema.org:
- Familiarize yourself with Schema.org, which is a collaborative project between major search engines (Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex) to create a standard vocabulary for structured data markup. Schema.org provides a comprehensive list of schemas (types) and properties that you can use to mark up your content.
- Identify Appropriate Schemas:
- Identify the relevant schemas that correspond to the content on your website. There are schemas available for various types of content, including articles, reviews, products, events, organizations, and more. Choose schemas that best describe the content you want to mark up.
- Implement Markup:
- Add schema markup to your web pages using JSON-LD (recommended), RDFa, or Microdata formats. JSON-LD is the preferred method by search engines because it’s easy to implement and maintain, and it doesn’t clutter your HTML code. Place the schema markup within the <script> tags in the <head> section of your webpage.
- Include Required Properties:
- Include the required properties for each schema type you’re using, as specified in the Schema.org documentation. These properties provide essential information about your content, such as name, description, URL, author, date published, rating, price, and more.
- Enhance Rich Snippets:
- Use schema markup to enhance rich snippets in search engine results pages (SERPs). Depending on the schema type you use, rich snippets can include additional information such as star ratings, product prices, event dates, article thumbnails, and more, making your listings more visually appealing and informative.
- Test Markup with Structured Data Testing Tool:
- Test your schema markup using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool (deprecated, use Rich Results Test instead) or other structured data validation tools. These tools will check for errors, warnings, and suggestions related to your markup and ensure that it’s implemented correctly.
- Monitor Performance in Search Console:
- Monitor the performance of your rich snippets and schema markup in Google Search Console. Google Search Console provides insights into how your structured data is being interpreted and displayed in search results, as well as any errors or enhancements you can make.
- Keep Markup Up to Date:
- Regularly review and update your schema markup to ensure it accurately reflects the content on your website. As your content changes or new features are added, update your structured data accordingly to maintain its effectiveness.
Content Updates On Page SEO:
Regularly updating your website’s content is crucial for maintaining relevance, attracting and retaining visitors, and improving search engine rankings. Here’s how to approach content updates effectively:
- Perform Content Audits:
- Conduct regular content audits to assess the quality, relevance, and performance of existing content on your website. Identify outdated, low-performing, or duplicate content that needs to be updated, consolidated, or removed.
- Update Outdated Information:
- Review your content to identify any outdated information, statistics, or references. Update the content with the latest information, research findings, or industry trends to ensure its accuracy and relevance.
- Improve Readability and Formatting:
- Enhance the readability and formatting of your content to make it more engaging and accessible to your audience. Break up long paragraphs, use subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists to organize information, and incorporate visuals such as images, infographics, and videos to enhance comprehension.
- Optimize for Keywords and SEO:
- Identify opportunities to optimize your content for relevant keywords and SEO. Conduct keyword research to identify high-potential keywords related to your topic, and incorporate them naturally into your content, including headings, body text, meta tags, and image alt attributes.
- Add New Information and Insights:
- Add fresh information, insights, or perspectives to your existing content to provide value to your audience. Share new research findings, case studies, expert opinions, or personal experiences that enhance the depth and relevance of your content.
- Expand and Deepen Coverage:
- Expand and deepen the coverage of topics that are relevant to your audience’s interests and needs. Provide comprehensive, in-depth coverage of key subjects, and address common questions, concerns, or pain points to establish your authority and expertise in your niche.
- Add Internal and External Links:
- Incorporate internal links to other relevant pages on your website to improve navigation and user engagement. Additionally, include external links to reputable sources, references, or further reading to enhance credibility and provide additional value to your audience.
- Update Design and Visual Elements:
- Refresh the design and visual elements of your content to maintain a modern and visually appealing appearance. Update images, graphics, and multimedia elements, and ensure they’re optimized for fast loading and mobile responsiveness.
- Promote Content Updates:
- Promote your updated content across various channels, including social media, email newsletters, and industry forums or communities. Highlight the changes or improvements you’ve made to encourage users to revisit and engage with your content.
- Monitor Performance and Iterate:
- Monitor the performance of your updated content using analytics tools to track metrics such as traffic, engagement, and conversions. Use this data to identify what’s working well and where further improvements or adjustments may be needed.
URL Structure On Page SEO:
A well-structured URL is important for both search engine optimization (SEO) and user experience. Here are some key principles to follow when creating URL structures:
- Keep URLs Simple and Descriptive:
- Create URLs that are easy to read, understand, and remember. Use descriptive words that accurately reflect the content of the page, making it clear to users and search engines what the page is about.
- Use Keywords:
- Incorporate relevant keywords into your URLs, ideally near the beginning, to improve search engine visibility and indicate the topic or focus of the page. However, avoid keyword stuffing and keep URLs concise and meaningful.
- Separate Words with Hyphens:
- Use hyphens (-) to separate words in URLs, rather than underscores (_) or spaces. Hyphens are preferred by search engines and are more readable for users. For example, use “example.com/my-page” instead of “example.com/my_page” or “example.com/my page”.
- Keep URLs Short and Simple:
- Aim for concise URLs that convey the main idea of the page without unnecessary complexity or parameters. Shorter URLs are easier to share, remember, and type, and they tend to perform better in search engine results.
- Use Lowercase Letters:
- Use lowercase letters in URLs to maintain consistency and avoid case sensitivity issues. Most web servers treat uppercase and lowercase letters in URLs differently, which can lead to duplicate content issues if not handled properly.
- Avoid Dynamic Parameters:
- Minimize the use of dynamic parameters, such as session IDs, query strings, and parameters with long strings of numbers or random characters, in URLs. Static, keyword-rich URLs are preferred for SEO and user-friendliness.
- Organize URLs Hierarchically:
- Structure URLs in a hierarchical manner to reflect the organization of your website’s content. Use directories (folders) to group related pages and subdirectories to further organize content into logical categories.
- Maintain Consistency:
- Maintain consistency in your URL structure across your website to make it easier for users and search engines to navigate and understand. Use a consistent naming convention and structure for similar types of pages (e.g., product pages, blog posts, category pages).
- Canonicalize URLs:
- Set up canonical URLs to specify the preferred version of a page when multiple URLs point to the same content (e.g., www vs. non-www, HTTP vs. HTTPS). This helps prevent duplicate content issues and consolidates link equity for SEO purposes.
- Optimize for Readability and Usability:
- Prioritize readability and usability when crafting URLs. Avoid using cryptic or meaningless strings of characters, and instead, use clear, descriptive words that accurately represent the content of the page.
Analytics and Monitoring On Page SEO:
Analytics and monitoring are essential components of any digital marketing strategy, allowing you to track and measure the performance of your website, content, and marketing campaigns. Here’s how to effectively utilize analytics and monitoring tools:

- Set Clear Goals and KPIs:
- Define clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your overall business objectives. These may include metrics such as website traffic, conversions, engagement, and ROI.
- Choose the Right Analytics Tools:
- Select analytics tools that provide the data and insights you need to measure and analyze performance effectively. Google Analytics is a popular and comprehensive choice for website analytics, but there are also other tools available depending on your specific requirements.
- Implement Tracking Codes:
- Install tracking codes, such as the Google Analytics tracking code, on your website to collect data on user behavior, traffic sources, conversions, and more. Ensure that tracking is correctly implemented across all pages of your website.
- Monitor Key Metrics:
- Regularly monitor key metrics and performance indicators to track progress towards your goals. This may include website traffic, page views, bounce rate, average session duration, conversion rate, and revenue.
- Segment and Analyze Data:
- Segment your data to gain deeper insights into different audience segments, traffic sources, and user behavior patterns. Analyze trends, identify opportunities, and uncover areas for improvement based on your data analysis.
- Track Conversions and Goals:
- Set up conversion tracking to measure the success of specific actions or goals on your website, such as form submissions, purchases, downloads, or sign-ups. Track the conversion paths and behaviors of users who complete these actions.
- A/B Testing:
- Conduct A/B tests to experiment with different variations of your website, content, or marketing campaigns. Test different elements, such as headlines, calls to action, landing page designs, or ad copy, and measure the impact on conversion rates and other KPIs.
- Monitor Website Performance:
- Monitor website performance metrics, such as page load times, server response times, and uptime, to ensure optimal website performance and user experience. Address any issues or bottlenecks that may impact performance.
- Stay Updated with Alerts:
- Set up alerts and notifications to stay informed about significant changes or anomalies in your website or campaign performance. This allows you to respond quickly to issues or capitalize on opportunities as they arise.
- Regular Reporting and Analysis:
- Generate regular reports summarizing key metrics, trends, and insights from your analytics data. Use these reports to communicate progress, identify areas for improvement, and inform decision-making across your organization.
- Continuous Optimization:
- Use data-driven insights to continuously optimize your website, content, and marketing strategies. Test new ideas, iterate based on performance data, and refine your approach to achieve better results over time.
Implementing these on-page SEO steps can help improve your website’s visibility in search engine results and attract more organic traffic. If you have any specific questions about any of these steps, feel free to ask!






[…] Search engine optimization (SEO) is essential for improving your blog’s visibility and attracting organic traffic. Incorporate relevant keywords throughout your blog post, including in the headline, subheadings, meta description, and body content. However, avoid keywrd stuffing, as this can negtively impact your search rankings. Write descriptive and compelling meta titles and descriptions to encourage clicks from search engine results pages. […]
[…] sites, exploring their significance, best practices, and how to leverage them effectively in your SEO […]
[…] link building is crucial for SEO, there are common mistakes that can undermine your […]
[…] The Links report provides insights into your site’s linking profile, which is crucial for SEO. […]
[…] niche or industry. Participating in unrelated forums can be seen as spammy and may not yield any SEO […]
[…] blogs, and content-sharing websites, to achieve several goals. These goals often include improving search engine optimization (SEO), building backlinks, increasing brand awareness, and driving traffic to a website. Here’s a […]
[…] field crucial for any website aiming to rank high on search engine results pages (SERPs). While on page SEO focuses on optimizing elements on your website, off-page SEO involves strategies that happen […]
[…] businesses or content creators, understanding and optimizing SEO (search engine optimization) strategies is crucial to increasing organic traffic to your […]